A new analysis of data collected on Venus more than 30 years ago suggests the planet may currently be volcanically active.
A research group from Italy led by David Sulcanese of the Università d’Annunzio in Pescara, Italy, has used data from a radar mapping of Venus’s surface taken in the early 1990s to search for volcanic lava flow, finding it in two regions.
The discovery suggests that volcanic activity may be currently active and more widespread than was previously thought, supporting previous indirect evidence that there is volcanic activity on Venus.
The work is published in the journal Nature Astronomy.
Venus is sometimes called “Earth’s twin sister.” Though only slightly smaller than Earth, its CO2-dominated atmosphere has a massive greenhouse effect that bakes its surface at about 465°C (870°F).
Although billions of years ago, Venus’s surface and atmosphere was likely much like Earth today, with liquid water present, the ever-brightening sun and volcanic activity raised temperatures enough to evaporate all water from the planet, leading to a runaway greenhouse effect.
Today, Venus seems desiccated, broiling hot and seemingly dead, surrounded by dense clouds of sulfuric acid.
Between 1990 and 1992, the Magellan spacecraft, launched from NASA’s space shuttle in 1989, orbited Venus with an array of scientific instruments, dropping as low as 295 km above the planet’s surface.
Comparing Magellan’s first cycle of radar scans taken January–September 1992 [Earth time] to the third cycle taken from Sept. 1990 to May 1991, both of which had a mean resolution of 150 meters, the researchers performed a number of adjustments to make the comparisons useful, such as adjusting backscatter for different viewing angles.
Both these cycles of scans had a left-view angle from the satellite, whereas the second cycle had a right-looking approach.
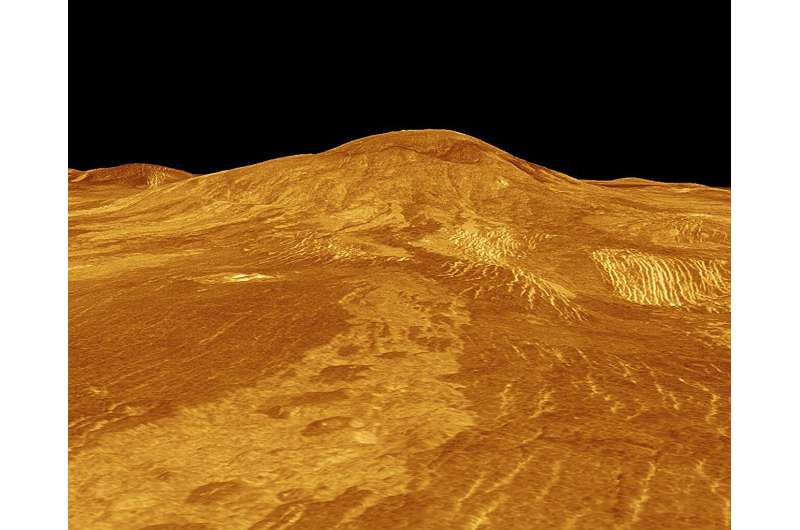
The first region encompasses lava flow features on the western flank of Sif Mons, a shield volcano at 22° north latitude on Venus that is a low-profile volcano that lies quite shallow on the ground, like the profile of a flat shield. The second region was the western part of Niobe Planitia at a similar latitude, 21° north, characterized by a flat terrain, many shield volcanoes and shield-related volcanic material.
After investigating a host of other possibilities for their observations, the group writes that their “best interpretation” of the observations is that the surface scattering properties of Venus, such as its roughness and composition, changed from the first cycle of scans to the third cycle, an interval of roughly 16 months. The changed features observed are probably explained, they write, as new lava flows that took place during the Magellan mission.